E-invoice – Basics:
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons have to prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars of invoice (in FORM GST INV-01) on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) and obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
After following above ‘e-invoicing’ process, the invoice copy containing inter alia, the IRN (with QR Code) issued by the notified supplier to buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’ in GST.
Because of the standard e-invoice schema (INV-01), ‘e-invoicing’ facilitates exchange of the invoice document (structured invoice data) between a supplier and a buyer in an integrated electronic format.
Please note that ‘e-invoice’ in ‘e-invoicing’ doesn’t mean generation of invoice by a Government portal.
There is no much difference indeed.
Registered persons will continue to create their GST invoices on their own Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems. These invoices will now be reported to ‘Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)’. On reporting, IRP returns the e-invoice with a unique ‘Invoice Reference Number (IRN)’ after digitally signing the e-invoice and adding a QR Code. Then, the invoice can be issued to the receiver (along with QR Code).
A GST invoice will be valid only with a valid IRN. 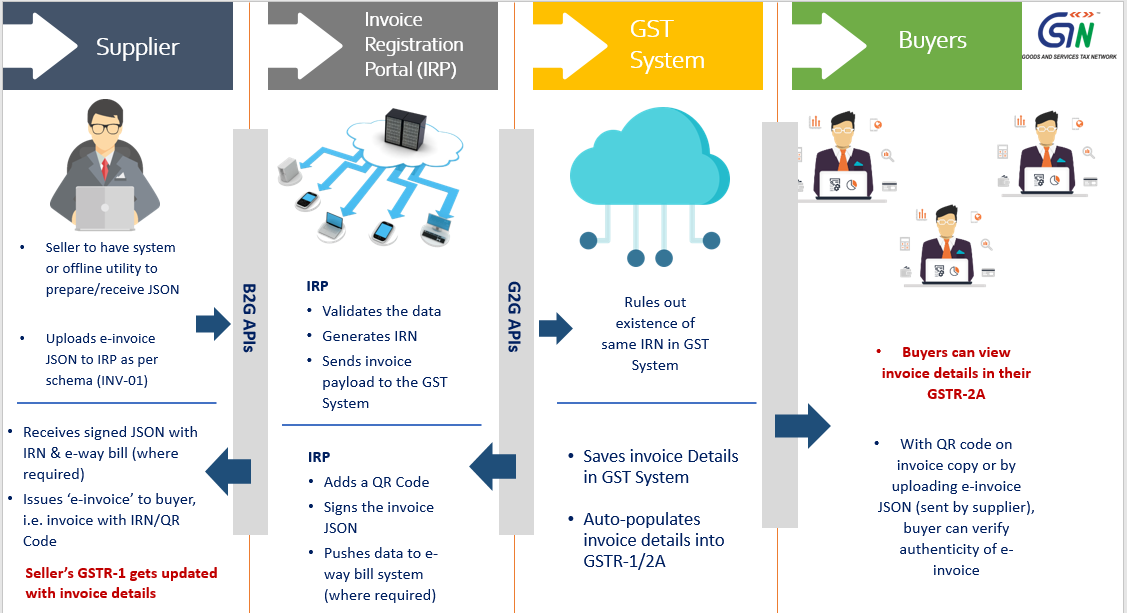
For more detailed process, please go through ‘e-invoice – Detailed Overview
For Registered persons whose aggregate turnover (based on PAN) in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 inwards, is more than prescribed limit (as per relevant notification), e-invoicing is mandatory.
Below notifications were issued on e-invoice:
68/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019
Central Goods and Services Tax (Eighth Amendment) Rules
Inserted below new sub-rules in Rule 48 of CGST Rules, 2017:
(4) The invoice shall be prepared by such class of registered persons as may be notified by the Government, on the recommendations of the Council, by including such particulars contained in FORM GST INV-01 after obtaining an Invoice Reference Number by uploading information contained therein on the Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portal in such manner and subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the notification.
(5) Every invoice issued by a person to whom sub-rule (4) applies inany manner other than the manner specified in the said sub-rule shall not be treated as an invoice.
(6) The provisions of sub-rules (1) and (2) shall not apply to an invoice prepared in the manner specified in sub-rule (4)
69/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019
Notified 10 Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portals for the purpose of preparation of invoice in terms of rule 48 (4)
70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019
Notified registered person, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds one hundred crore rupees, as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice in terms of sub-rule (4) of rule 48 of the said rules in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person; notification to come into force from the 1st day of April, 2020
(This notification superseded by 13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020)
2 of 2020 Dt. 1-1-2020
Substituted Form GST INV-1 as e-invoice schema
(Schema further amended vide Notification 60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020)
13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020(in supersession of 70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019)
e-invoicing to start from the 1st October, 2020;
Notifies registered persons, other than those referred to in sub-rules (2), (3), (4) and (4A) of rule 54 of the said rules, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds Rs. 100 Cr., as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice and other prescribed documents, in terms of sub-rule (4) of rule 48 of CGCT Rules, 2017, in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
(Further amended by 61/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020)
60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020
Central Goods and Services Tax (Ninth Amendment) Rules, 2020
New form substituted for GST INV-01 (i.e. notified revised Schema/format for e-invoice)
61/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020
Amended notification 13/2020 Dt. 21-3-2020
Special Economic Zone units also excluded from e-invoicing mandate
Aggregate Turnover of registered persons (required to prepare invoice in terms of Rule 48(4)) enhanced to Rs. 500 Cr
70/2020 Dt. 30-9-2020
the words “a financial year” in notification 13/2020 Dt. 21-3-2020 substituted with “any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards”
Invoices for exports were also included
In rule 46,after clause (q), below clause is inserted:
“(r) Quick Reference code, having embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, in case invoice has been issued in the manner prescribed under sub-rule (4) of rule 48.”
In rule 48, in sub-rule (4), below proviso was inserted:
“Provided that the Commissioner may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, exempt a person or a class of registered persons from issuance of invoice under this sub-rule for a specified period, subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the said notification.”
In rule 138A, for sub-rule (2), below sub-rule was substituted:
“(2) In case, invoice is issued in the manner prescribed under sub-rule (4) of rule 48, the Quick Reference (QR) code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, may be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the physical copy of such tax invoice
e-invoice has many advantages for businesses such as Auto-reporting of invoices into GST return, auto-generation of e-way bill (where required).
e-invoicing will also facilitate standardisation and inter-operability leading to reduction of disputes among transacting parties, improve payment cycles, reduction of processing costs and thereby greatly improving overall business efficiency.
Businesses will continue to issue invoices as they are doing now. Necessary changes on account of e-invoicing requirement (i.e. to enable reporting of invoices to IRP and obtain IRN), will be made /Accounting and Billing Software providers in their respective software.They need to get the updated version having this facility.
As per Rule 48(4), notified person has to prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars in FORM GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal and after obtaining Invoice Reference Number (IRN). As per Rule 48(5), any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.So, the document issued by notified person becomes legally valid only with an IRN. However, in the initial period of operation, Government has given a relaxation that invoices raised by notified taxpayers during October, 2020 without following e-invoice procedure (i.e. uploading invoice details on e-invoice portal (IRP), obtaining IRN and issuing invoice with QR Code) will be deemed to be valid and no penalty will be there if the IRN for such invoice s is obtained within 30 days of date of invoice . It was also specified that no such relaxation would be available for the invoices issued from 1st November 2020.